Converting mesh to mm and inches – understanding mesh size
 When working with powders, screens, or filtration systems, understanding mesh size—and how it converts to other units—is essential. Accurate conversions from mesh size to mm, mesh to mm, and mesh size to micron are critical in both industrial and scientific applications. Comparing inches vs mm is especially important when ensuring compatibility between international sizing standards and mesh specifications. When working with powders, screens, or filtration systems, understanding mesh size—and how it converts to other units—is essential. Accurate conversions from mesh size to mm and mesh size to micron are critical in both industrial and scientific applications. Comparing inches vs mm is especially important when ensuring compatibility between international sizing standards and mesh specifications.
When working with powders, screens, or filtration systems, understanding mesh size—and how it converts to other units—is essential. Accurate conversions from mesh size to mm, mesh to mm, and mesh size to micron are critical in both industrial and scientific applications. Comparing inches vs mm is especially important when ensuring compatibility between international sizing standards and mesh specifications. When working with powders, screens, or filtration systems, understanding mesh size—and how it converts to other units—is essential. Accurate conversions from mesh size to mm and mesh size to micron are critical in both industrial and scientific applications. Comparing inches vs mm is especially important when ensuring compatibility between international sizing standards and mesh specifications.
What does mesh size mean?
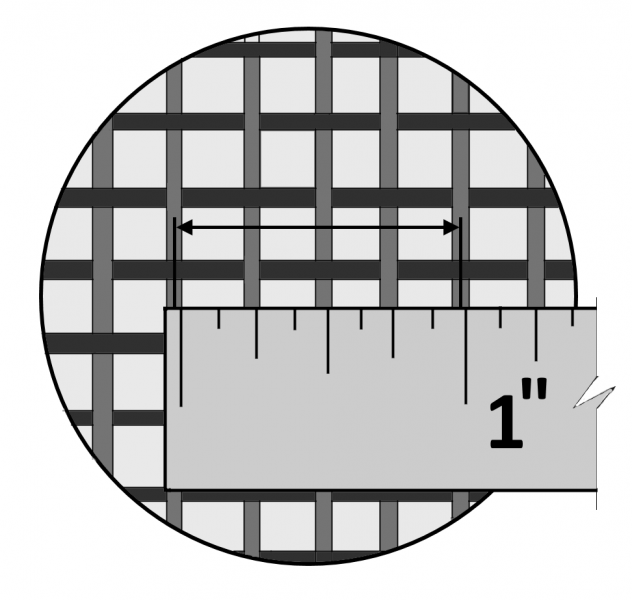
Mesh size is a measurement that tells us how many openings there are per linear inch in a screen or sieve. For instance, a 200 mesh size screen has 200 openings per inch, while an 80 mesh size screen has only 80 openings. As the mesh size increases, the openings become smaller, resulting in finer particles passing through.
To visualize this:
A 4-mesh screen has four large square openings across a single inch. Meanwhile, 100 mesh to mm translates to roughly 0.149 mm, and 100 mesh to microns equals 149 microns. So, mesh size is not a precise measurement of particle size, but rather a general guide, which is why conversions like mesh size to mm or mesh size to microns are often necessary.
What do the minus (-) and plus (+) plus signs mean when describing mesh sizes?
The symbols "+" and "–" in screen mesh sizes indicate particle behavior:
- -200 mesh size: Particles pass through a 200 mesh size screen.
- +200 mesh size: Particles remain on a 200 mesh size screen.
A description such as "-40+100 Mesh" means that the particles passed through a 40 mesh screen but were retained on a 100 mesh screen. These particles are smaller than 420 microns but larger than 100 mesh to microns, or 149 microns. The inclusion of "+" in specifications is common when controlling for both lower and upper size limits.
How fine do screens get?
The ultimate fineness of a screen depends on the mesh diameter—the thickness of the wire used. The finer the wire, the smaller the particle it can screen. For screens finer than 325 mesh to micron (~44 microns), the industry often uses microns to mesh conversions for better precision.
Higher mesh sizes, such as 400 mesh to micron (37 microns), go beyond the limits of physical screens and are more accurately described using mesh micron and size mm data.
Inches vs mm
In materials handling and engineering, converting between inches vs mm is essential. Many measurements are still given in inches, but scientific accuracy often demands mesh size to mm conversions. Whether calculating the mesh size to micron or determining the correct screen frame for a 200 mesh size material, accurate measurement is key.
You’ll notice mesh size to mm and mesh size to microns are closely related. These help engineers and quality controllers convert values quickly using a mesh converter.
Mesh conversion tools and use cases
Using a mesh converter simplifies the process of switching between units like microns, mm, and inches. Whether converting 1 mesh mm or a complex specification like 200 mesh to micron, digital tools ensure accuracy and speed.
Applications include:
- Sorting materials using screen mesh sizes
- Determining mesh diameter for weaving screens
- Matching international specs using mesh scale
- Comparing size mm between suppliers
- Translating microns to mesh and vice versa
These tools often rely on standard reference tables but may also be programmable calculators that work well for both inches vs mm and mesh size to micron calculations.
Understanding mesh size and mastering how to convert mesh size to mm or mesh size to micron ensures accuracy in both design and application. Whether you're dealing with 80 mesh size or a fine 200 mesh size, knowing how to switch between inches vs mm is crucial for seamless communication across industries.
Detailed mesh size conversion chart
The following table provides a comprehensive conversion between mesh sizes, microns, millimeters (mm), mils, and inches:
| Mesh Size | Microns | Mm | Mils | Inches |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4760 | 4,76 | 187,5 | 0,1875 |
| 6 | 3360 | 3,36 | 152,3 | 0,1523 |
| 8 | 2380 | 2,38 | 93,7 | 0,0937 |
| 10 | 1680 | 1,68 | 66,1 | 0,0937 |
| 12 | 1410 | 1,41 | 55,5 | 0,0555 |
| 14 | 1190 | 1,19 | 46,8 | 0,0468 |
| 16 | 1000 | 1 | 33 | 0,0333 |
| 20 | 840 | 0,84 | 33,1 | 0,0331 |
| 24 | 710 | 0,71 | 27,9 | 0,0279 |
| 28 | 590 | 0,59 | 23,2 | 0,0232 |
| 32 | 500 | 0,5 | 19,7 | 0,0197 |
| 35 | 420 | 0,42 | 16,5 | 0,0165 |
| 42 | 350 | 0,35 | 13,7 | 0,0137 |
| 48 | 297 | 0,297 | 11,7 | 0,0117 |
| 60 | 250 | 0,25 | 9,8 | 0,0098 |
| 65 | 210 | 0,021 | 6,9 | 0,0069 |
| 80 | 177 | 0,177 | 5,9 | 0,0059 |
| 100 | 149 | 0,149 | 4,9 | 0,0049 |
| 115 | 125 | 0,125 | 4,1 | 0,0041 |
| 150 | 105 | 0,105 | 3,4 | 0,0034 |
| 170 | 88 | 0,088 | 2,9 | 0,0029 |
| 200 | 74 | 0,074 | 2,4 | 0,0024 |
| 250 | 62 | 0,062 | 2,1 | 0,0021 |
| 270 | 53 | 0,053 | 1,7 | 0,0017 |
| 325 | 44 | 0,044 | 1,2 | 0,0012 |
| 400 | 37 | 0,037 | ||
| 477 | 31 | 0,031 | ||
| 565 | 26,2 | 0,026 | ||
| 673 | 22 | 0,22 | ||
| 800 | 18,5 | 0,019 | ||
| 949 | 15,6 | 0,016 | ||
| 1346 | 11 | 0,011 | ||
| 1590 | 9,3 | 0,0093 | ||
| 1898 | 7,8 | 0,0078 | ||
| 2280 | 6,5 | 0,0065 | ||
| 2690 | 5,5 | 0,0055 | ||
| 3200 | 4,6 | 0,0046 | ||
| 3800 | 3,9 | 0,0039 | ||
| 4480 | 3,3 | 0,0033 | ||
| 5280 | 2,8 | 0,0028 | ||
| 6430 | 2,3 | 0,0023 | ||
| 7590 | 1,95 | 0,00195 | ||
| 9030 | 1,65 | 0,00165 | ||
| 10730 | 1,38 | 0,00138 | ||
| 12780 | 1,16 | 0,00116 | ||
| 18000 | 0,82 | 0,00082 |
This chart is instrumental in converting mesh size to mm and understanding the corresponding particle sizes. For instance, converting 0.25 inch to mm yields 6.35 mm, which aligns with a mesh size of approximately 3. Similarly, 0.05 inch to mm is about 1.27 mm, correlating with a mesh size near 16.
Practical applications of mesh size conversions
In various industries, understanding mesh size to micron conversions is vital. For example:
- 100 mesh to microns equates to 149 microns, suitable for fine filtration processes.
- 100 mesh to mm is approximately 0.149 mm, relevant in powder processing.
- 20 mesh to micron conversion results in 841 microns, used in coarse screening.
- 200 mesh to micron is 74 microns, essential for fine particle separation.
- 325 mesh to micron equals 44 microns, applicable in ultra-fine filtration.
- 400 mesh to micron is 37 microns, used in high-precision applications.
These conversions aid in selecting the appropriate mesh scale for specific applications, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in processes.
Additional size conversions
Understanding various size conversions is crucial:
- 26 inch to mm: 660.4 mm
- 36 inch to mm: 914.4 mm
- 42 inches in mm: 1066.8 mm
- 48 inch to mm: 1219.2 mm
- 60 mils to mm: 1.524 mm
These conversions are essential when dealing with equipment dimensions and material specifications.





